Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing
The process
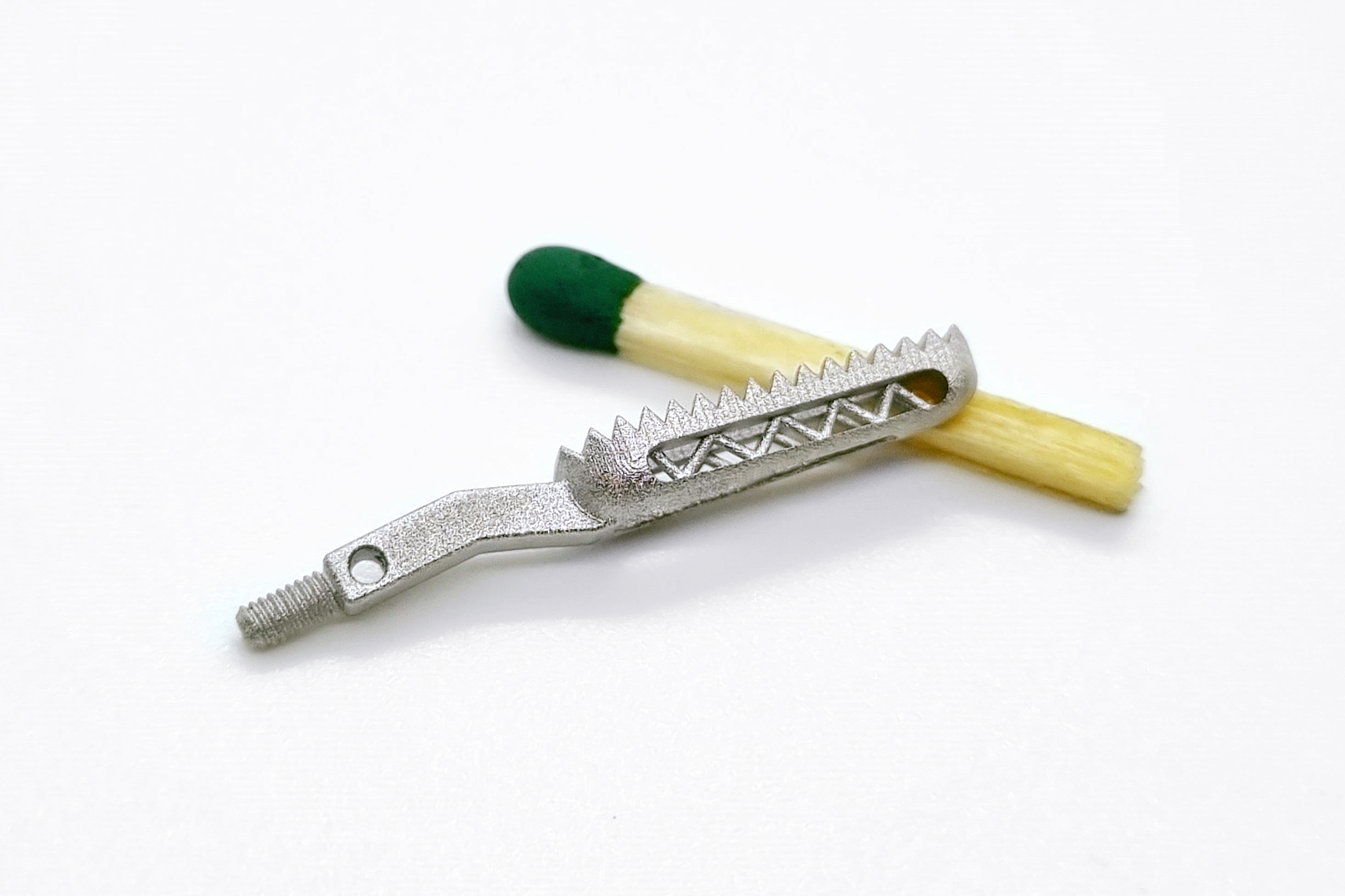
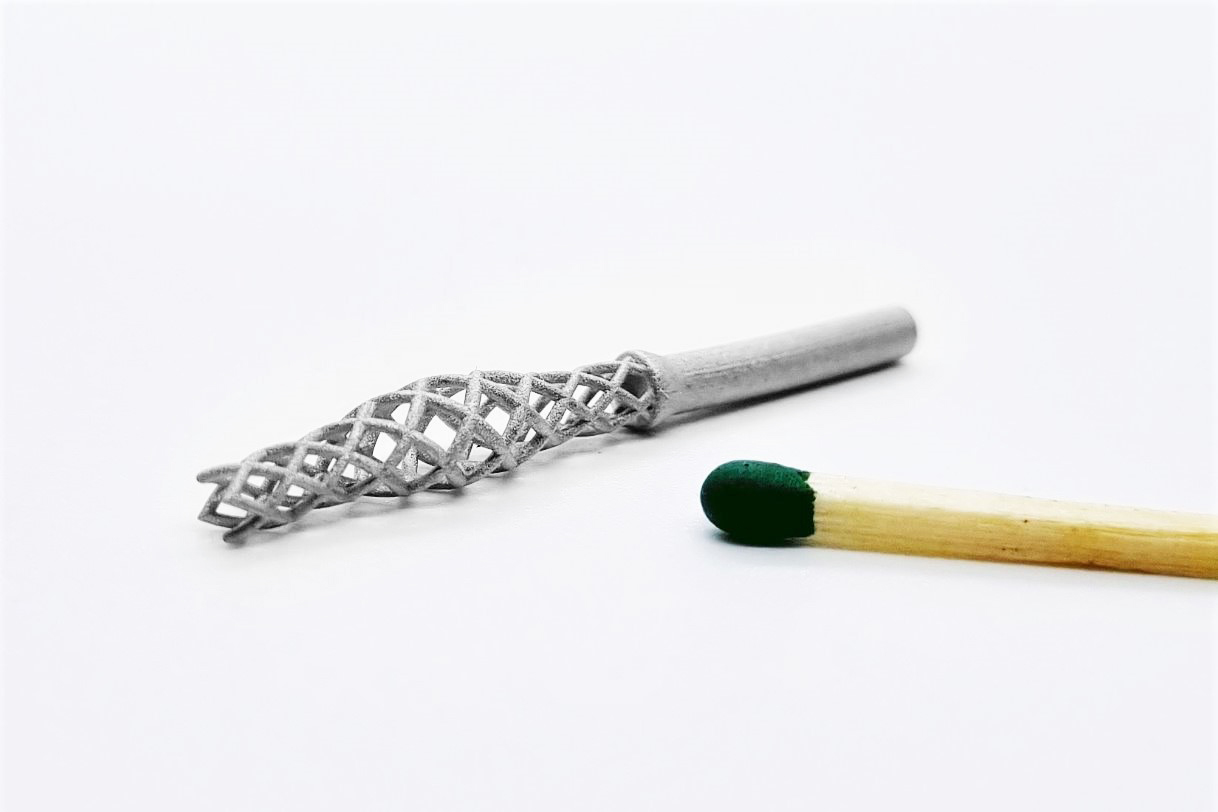
Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing (LMM) is a process for manufacturing high-precision, small metal components. In this process, the starting material consisting of metal powder and a photopolymer is stored in a material container. The mixture has a "butter like" consistency at room temperature. When heated, it becomes liquid and can be applied evenly and in thin layers to the building platform with the aid of a heated coating blade. This is locally exposed by a projector and the photopolymer hardens in the exposed areas. This process is repeated layer by layer until a Grünling is formed. To remove the Grünling from the material block, it is heated to about 50 °C, causing the unexposed material to melt and flow off. The material mixture that has flowed off can be reused for further printing processes without loss. Thermal debinding of the photopolymer and sintering of the parts are carried out in a two-stage process. The sintered parts are approx. 20 % smaller than the printed Grünling, whereby the exact sintering shrinkage factor depends on the material composition used and has very good reproducibility.
Find out more about this process on MetShape's merchant profile.
Advantages
- Highest resolution without distorting edge effects
- Low tolerances
- Production of thin-walled and distortion-sensitive components
- High surface quality
- Low rework
- Equal surfaces on all sides
- No support structures
- Joining of assemblies in the sintering process
LMM Process in Application
The advantages of LMM technology are in particular the high resolution and precision as well as the good surface quality, whereby small, complex and filigree components can be produced in previously unattainable quality. In addition, LMM technology does not require any support structures and the components can be arranged three-dimensionally in the installation space.
LMM components have a very high final contour and surface quality, which is why time-consuming and costly reworking can be reduced to a minimum. With the LMM process, small quantities, a high number of variants and thus high flexibility of the respective component spectrum are possible without storage costs.
In addition to the widespread applications in prototype and one-off production, the sinter-based additive manufacturing processes will increasingly offer alternatives to conventional production in the aerospace, medical technology and jewelry sectors for small to medium quantities. Another area of application is tool manufacturing, where traditional production is relatively cost-intensive due to high complexity and low volumes.
Technical Information
- Max. Component size: 70 x 45 x 100 mm
- Lateral resolution: 35 µm
- Layer thickness: 10 - 60 µm
- Build rate up to 250 layers/h
- Build rate up to 100 cm³/h
Limitations
- Not suitable for medium and large components



 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Italiano
Italiano
